Are you over 21 years of age?
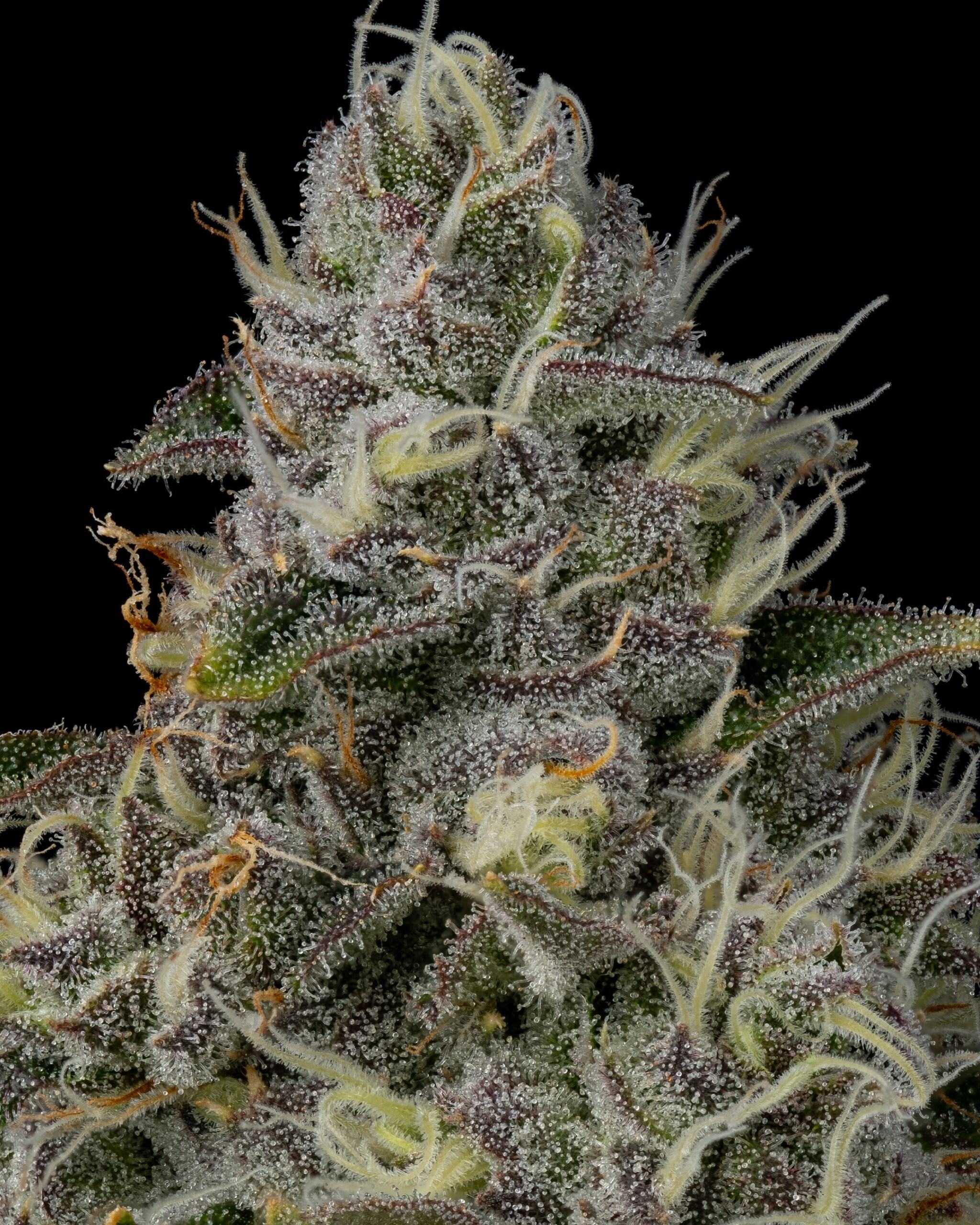
Cannabis is renowned for its therapeutic and recreational benefits. The adventure begins with understanding the importance of female plants. Unlike their male counterparts, which produce pollen, female cannabis plants are prized for their buds rich in cannabinoids like THC and CBD. These buds are the heart of the cannabis experience, offering the desired effects and benefits.
The growing process unfolds in several stages. It all starts with germination, where seeds sprout and roots begin to form. As the seedlings grow, they enter the vegetative stage, focusing on developing leaves and stems. This phase is crucial for building a strong foundation. Next comes the flowering stage, where the magic happens—buds begin to form, promising a bountiful harvest. Once the buds mature, it’s time for harvesting, followed by the meticulous processes of drying and curing to enhance the quality and potency of the cannabis. Finally, the cycle concludes with pruning and preparing for the next round of growth.
Choosing the right growing medium is another critical decision. Hydroponics offers a high-tech approach, using nutrient-rich water solutions to accelerate growth and boost yields. However, it requires careful monitoring and a higher initial investment. On the other hand, living soil embraces a more natural method, fostering a rich ecosystem of beneficial microbes. This approach often results in superior flavor and sustainability, though it may yield less and take longer.
The environment in which cannabis is grown also plays a significant role. Outdoor growing harnesses the power of natural sunlight, making it cost-effective but subject to the whims of nature. Greenhouse growing strikes a balance, combining natural light with a controlled environment to protect plants and optimize yields. Mixed light setups blend natural and artificial light, extending the growing season and enhancing growth. Finally, indoor growing offers complete control over all environmental factors, often producing the highest quality cannabis, albeit at a higher cost.


Cannabis flowers are gently soaked in ethanol, a clear and pure solvent. As the ethanol mingles with the plant material, it dissolves the precious cannabinoids and terpenes, creating a rich, green solution. This mixture is then filtered to remove any plant debris, leaving behind a potent liquid. The final step involves evaporating the ethanol, revealing a concentrated extract ready to be transformed into tinctures, edibles, or full-spectrum oils.
Carbon dioxide is pressurized and heated until it reaches a supercritical state, neither fully liquid nor gas. This supercritical CO2 is then passed through the cannabis material, acting as a solvent to extract cannabinoids and terpenes. The process is meticulously controlled, ensuring that only the desired compounds are captured. Once the extraction is complete, the CO2 is safely removed, leaving behind a pure, amber-colored extract. This extract is often used to create distillates, vape oils, and other high-purity products.
In a specialized extraction room, butane or propane is used to create some of the most potent cannabis concentrates. The process begins with cannabis flowers being placed in a closed-loop system. Butane is introduced, dissolving the cannabinoids and terpenes from the plant material. The solution is then purged of butane through a careful heating process, ensuring no residual solvents remain. The result is a variety of textures and consistencies, from glass-like shatter to creamy wax and flavorful live resin, each capturing the essence of the cannabis plant.
A cool room is where ice water extraction takes place. Fresh cannabis flowers are submerged in ice-cold water, and the mixture is gently agitated. The cold temperature causes the trichomes, tiny resin glands rich in cannabinoids and terpenes, to break off from the plant material. This mixture is then filtered through a series of fine mesh bags, each capturing different sizes of trichomes. The collected trichomes are dried, resulting in a product known as bubble hash, a potent and flavorful concentrate.
Cannabis flowers or water hash are placed between sheets of parchment paper. Using a rosin press, heat and pressure are applied, causing the cannabinoids and terpenes to ooze out as a sticky, golden resin. This solventless method preserves the natural profile of the plant, resulting in a pure and aromatic concentrate known as rosin. The simplicity and purity of this process make it a favorite among connoisseurs.
In a sophisticated lab, the creation of THCA diamonds begins with a high-quality cannabis extract, often live resin. This extract is placed in a sealed jar and left undisturbed for several weeks. During this time, the THCA slowly crystallizes, forming sparkling diamonds. These diamonds are often combined with terpene-rich sauce, creating a product that is both visually stunning and incredibly potent. The patience and precision required for this process result in one of the most sought-after cannabis concentrates.


Flower: The part of the cannabis plant that is harvested and consumed for its psychoactive and medicinal properties.
Grow Process: The cultivation of cannabis plants, which involves several stages from seed to harvest.
Want Female Plants, Not Male Plants: Female plants produce the buds that are rich in cannabinoids, while male plants are typically removed to prevent pollination and seed production.
Usually Grown from Clones, Taken from Mother Plants: Cloning involves taking cuttings from a mature “mother” plant to produce genetically identical plants.
Veg Phase: The vegetative phase where the plant focuses on growing leaves and stems.
Flower Phase: The flowering phase where the plant produces buds.
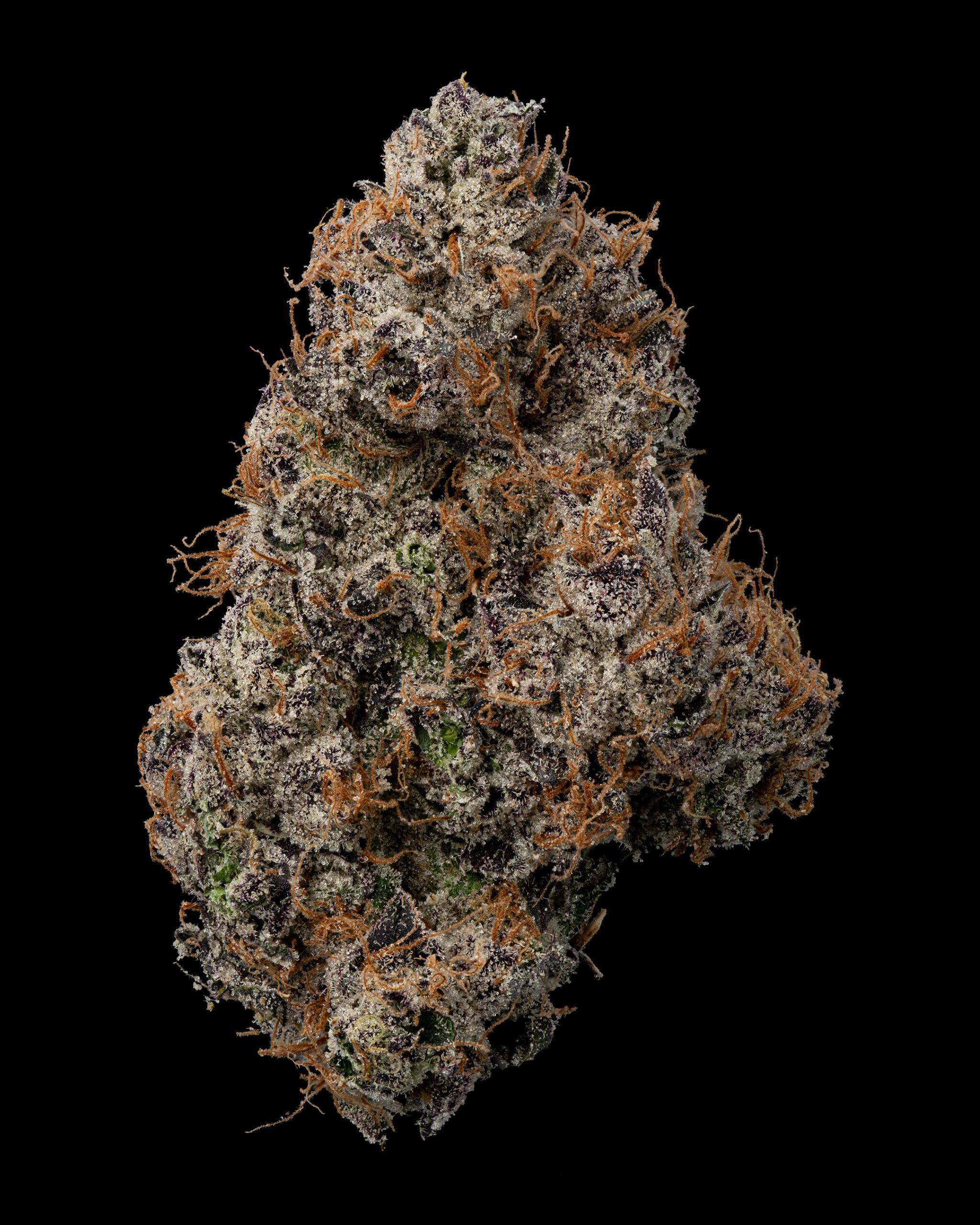
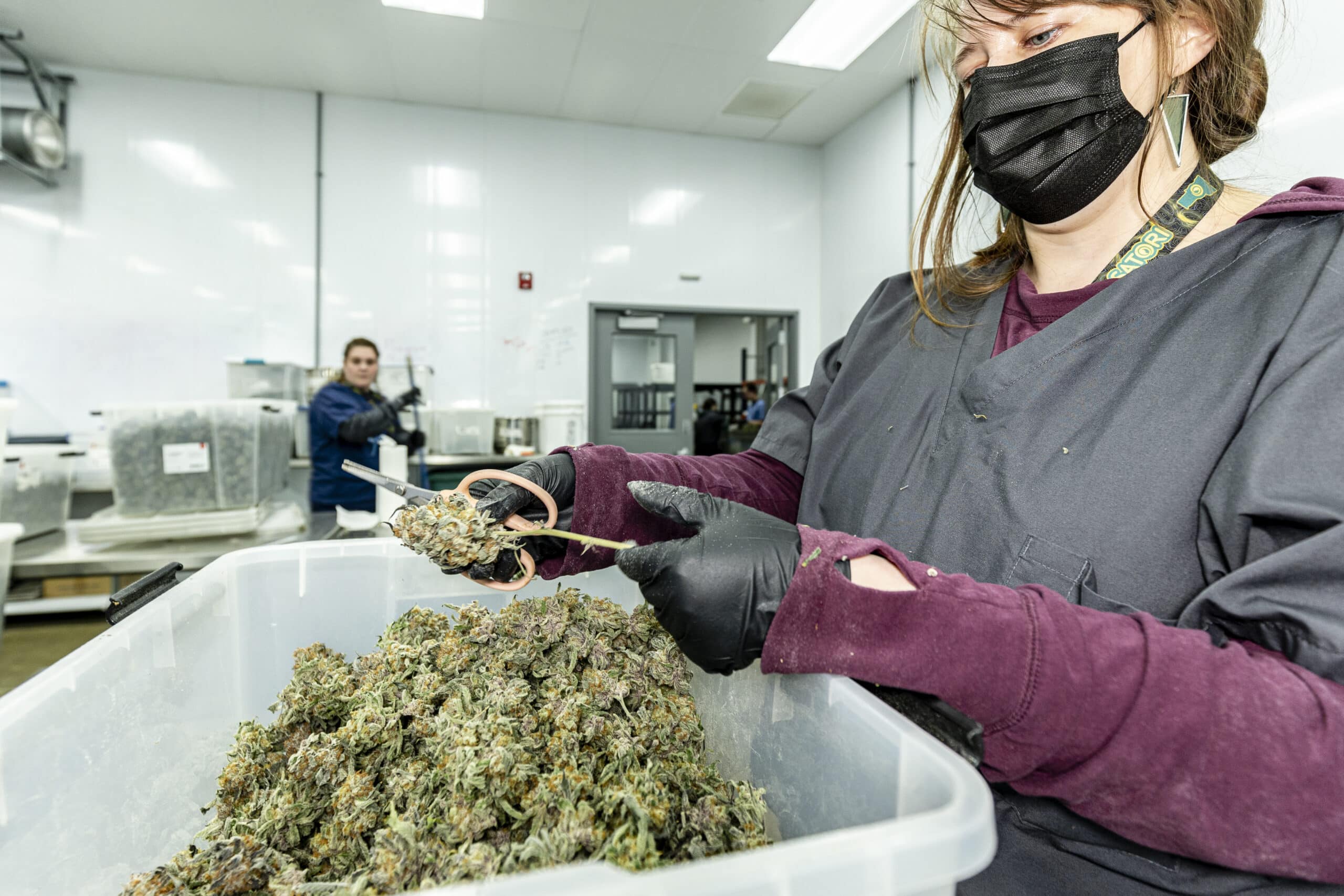
Harvest: The process of cutting down the mature cannabis plants to collect the buds.
Dry and Cure: Drying removes moisture from the buds, and curing enhances flavor and potency by allowing the buds to age in a controlled environment.
Trim: Removing excess leaves and stems from the buds to improve appearance and quality.
Cross Breeding, Genetic Modification: Techniques used to create new cannabis strains with desired traits by combining genetics from different plants.
Aromatic compounds found in cannabis that contribute to its flavor and effects.
Chemical compounds in cannabis that interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system.
The process of separating cannabinoids and terpenes from the cannabis plant.
